Gibbs sampling
Gibbs sampling is another MCMC technique used for sampling.
MCMC Overview
The purpose of MCMC techniques is to blanket the sample space with a markov chain, who’s stationary distribution is equal to the probability distribution of the sample space. Why do we develop these techniques just to sample a distribution? Well, if you have a multivariable distribution, then sampling the vanilla way would require you to marginalize over multiple variables, which becomes infeasible since marginalizing grows exponentially.
The following image is a simple Markov Chain, and its transition matrix.
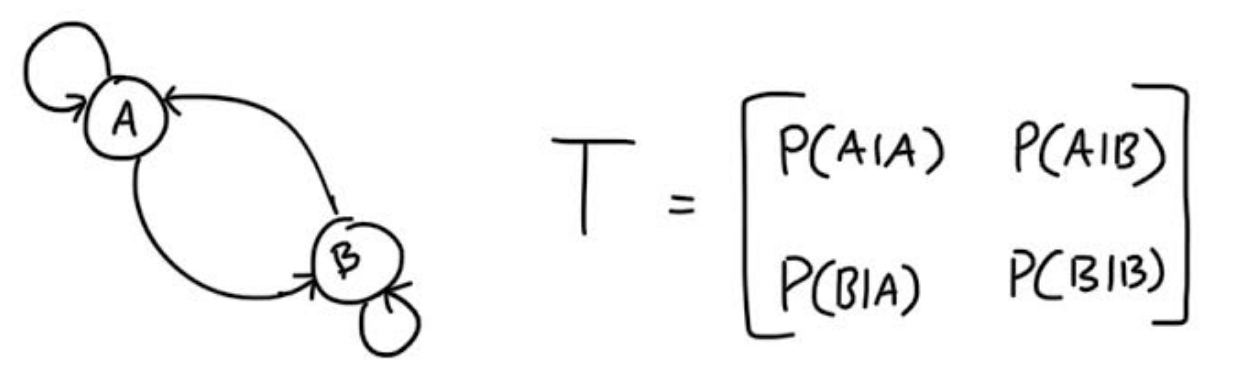
The representing the Markov Chain as a transition matrix is useful because when we have our current state vector S, we can multiply the Transition Matrix to it, and obtain the new state vector.
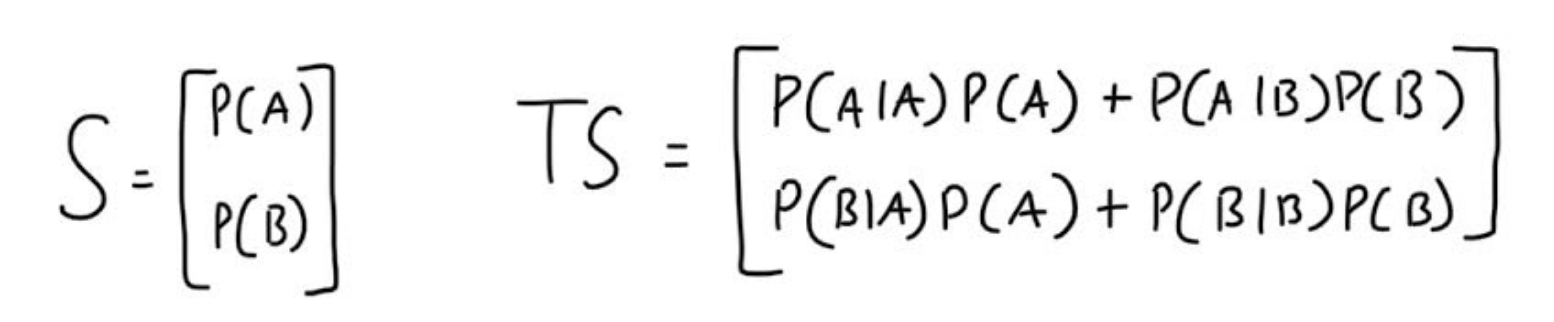
If we constructed our Markov Chain such that its steady state distribution is equal to our desired distribution of A and B. Then we can write P(A) as
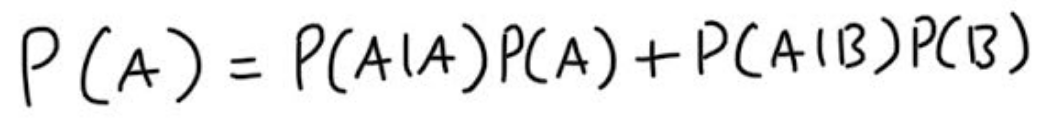
and B can be written similarly.
Therefore, we need to find the right transition probabilities such that traversing this Markov Chain will produce representative samples.
Gibbs Procedure
Here are the steps Gibbs uses to sample from a 3 variable distribution.
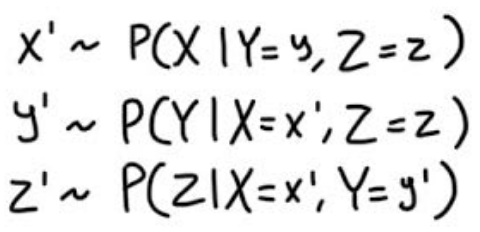
Each sample is just sampling from a 1 dimensional distribution, which can be done using multiple techniques such as rejection sampling.
So why does this work? Observe the following steps for our 3 variable cases. The first line is a repeat of our previous example of P(A), and substituting the conditional probabilities with the Gibbs sampling equations.
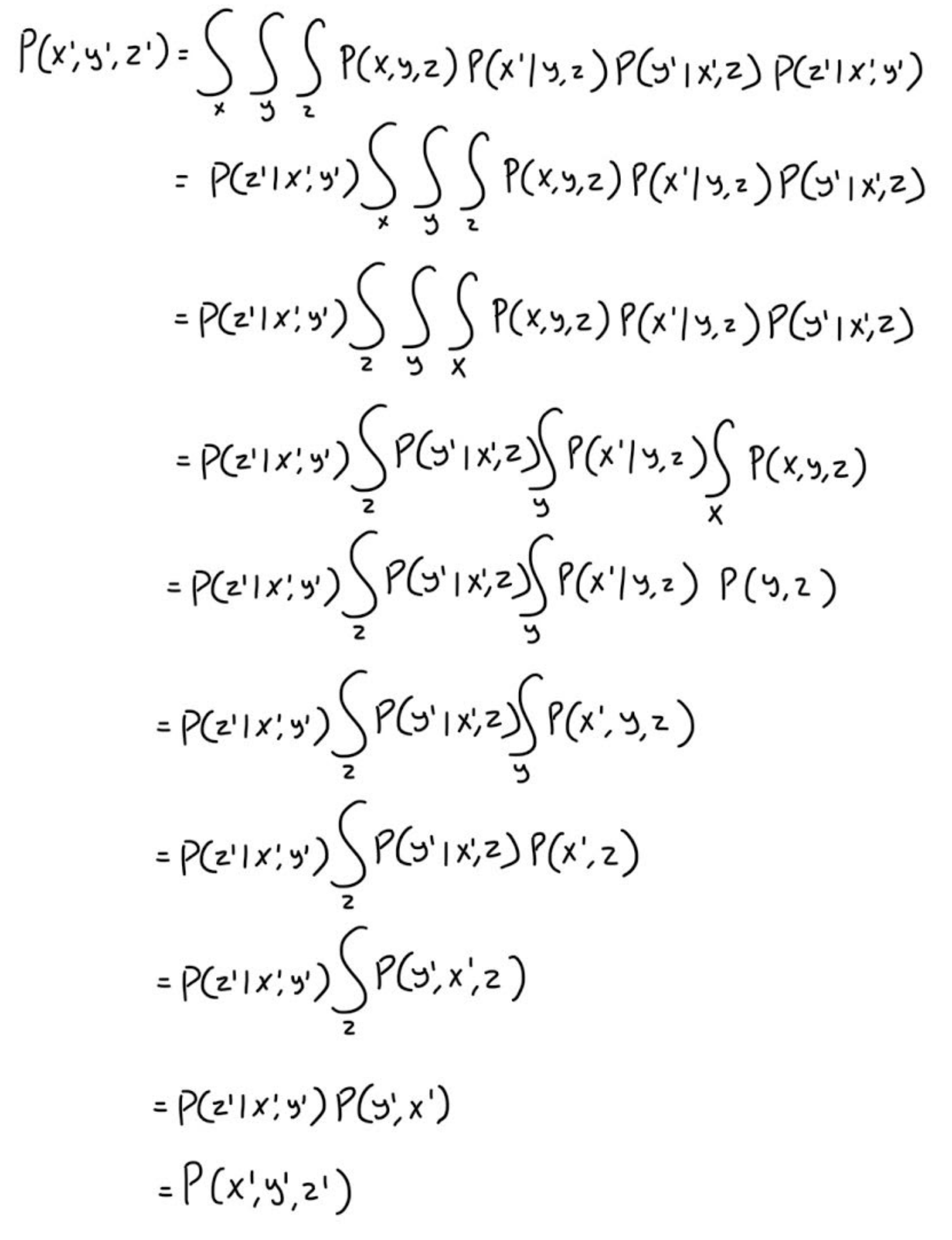
This shows that the steps Gibbs uses do indeed produce the right transition probabilities to make our Markov Chain’s steady state distribution equal the actual probability distribution that we are trying to sample from.
Additional Notes
There is a variation of Gibbs Sampling that I see used in LDA and other topics, called Collapsed Gibbs. As the names suggests it “A collapsed Gibbs sampler integrates out (marginalizes over) one or more variables when sampling for some other variable” (Wikipedia).
References
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gibbs_sampling#Collapsed_Gibbs_sampler https://www.cs.cmu.edu/~epxing/Class/10708-14/scribe_notes/scribe_note_lecture18.pdf https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rejection_sampling